Autoimmune Diseases: When the Body Turns Against Itself
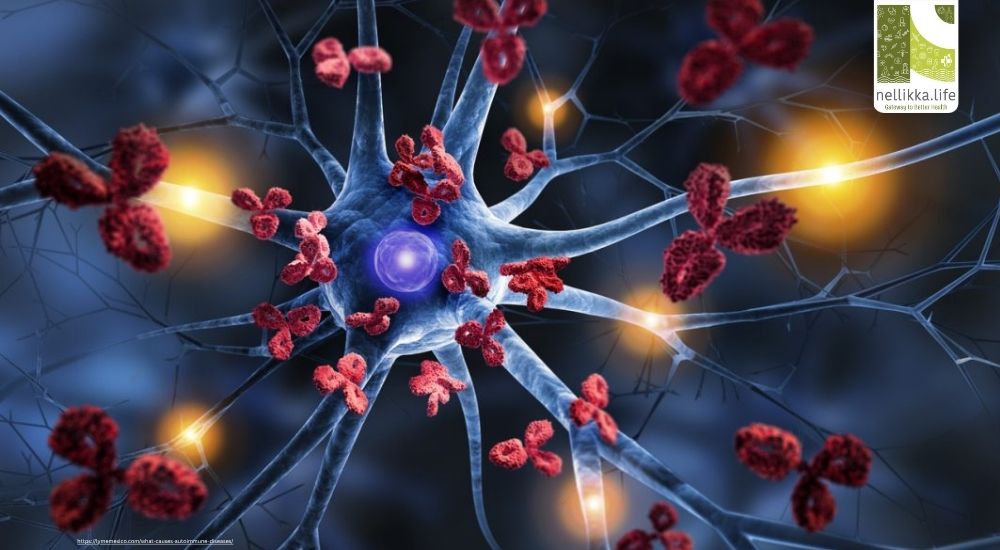
Our immune system is designed to protect us — it recognizes and attacks foreign invaders such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
But what happens when this defense system mistakenly attacks your own body?
That’s the essence of autoimmune disease — a group of disorders where the immune system loses the ability to distinguish between “self” and “non-self,” leading to chronic inflammation, tissue damage, and dysfunction of vital organs.
What Are Autoimmune Diseases?
An autoimmune disease occurs when the body’s immune system — which normally protects against infections — mistakenly targets healthy cells and tissues.
This abnormal immune response results in inflammation and damage to specific organs or multiple systems simultaneously.
There are more than 80 known autoimmune diseases, ranging from mild to life-threatening. Some are organ-specific (like Type 1 diabetes), while others are systemic (like lupus).
How Does It Occur?
Immune System Malfunction
Normally, the immune system identifies self-cells using special surface proteins. In autoimmune diseases, this recognition fails — autoantibodies and autoreactive T-cells attack the body’s own tissues.
Genetic Susceptibility
Certain genes (especially those in the HLA region) increase vulnerability. If autoimmune conditions run in your family, you may be genetically predisposed.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors often “trigger” the immune attack in genetically susceptible individuals:
- Viral or bacterial infections
- Hormonal changes (especially in women)
- Chronic stress
- Certain medications
- Exposure to toxins or pollutants
Molecular Mimicry
Some microbes resemble human cells. When the immune system fights the infection, it may mistakenly attack similar-looking body tissues, a phenomenon known as molecular mimicry (seen in diseases like rheumatic fever).
Common Autoimmune Diseases and Their Target Organs
| Disease | Target Area | Key Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) | Joints | Pain, swelling, stiffness, joint deformity |
| Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) | Skin, kidneys, brain, joints | Fatigue, rash, joint pain, kidney issues |
| Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus | Pancreas | Increased thirst, frequent urination, weight loss |
| Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis | Thyroid gland | Fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance |
| Graves’ Disease | Thyroid gland | Weight loss, anxiety, heat intolerance |
| Multiple Sclerosis (MS) | Nervous system | Muscle weakness, vision problems, numbness |
| Psoriasis / Psoriatic Arthritis | Skin, joints | Scaly skin patches, joint inflammation |
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease (Crohn’s / Ulcerative Colitis) | Gut | Abdominal pain, diarrhea, blood in stool |
| Celiac Disease | Small intestine | Bloating, diarrhea, malabsorption |
| Sjögren’s Syndrome | Salivary and tear glands | Dry eyes, dry mouth |
What Causes Autoimmune Diseases to Flare Up?
Autoimmune conditions often alternate between flare-ups (active inflammation) and remission (symptom-free periods).
Common triggers include:
- Infections
- Lack of sleep or high stress
- Hormonal changes (menstrual cycles, pregnancy, menopause)
- Certain foods (in gluten sensitivity or celiac disease)
- Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light (for lupus)
Symptoms: How to Recognize an Autoimmune Disorder
While symptoms vary depending on the specific disease, many share common signs:
General Symptoms
- Chronic fatigue
- Low-grade fever
- Joint or muscle pain
- Skin rashes
- Brain fog or concentration issues
- Hair loss
- Numbness or tingling sensations
Organ-Specific Symptoms
- Thyroid disorders: Weight fluctuation, heat/cold intolerance
- Type 1 Diabetes: Frequent urination, excessive thirst
- Lupus/RA: Joint stiffness, skin rash
- IBD: Diarrhea, abdominal pain, weight loss
Persistent, unexplained symptoms — especially joint pain, fatigue, or skin changes — should never be ignored.
Diagnosis
There’s no single test for autoimmune diseases, but doctors may use a combination of:
- Blood tests: ANA (Antinuclear Antibody), ESR, CRP, rheumatoid factor, thyroid antibodies
- Imaging: X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound for inflammation
- Biopsy: In specific organs like skin, kidney, or gut
Treatment & Management
While autoimmune diseases are not fully curable, they can be controlled effectively with early diagnosis and the right treatment plan:
1. Medications
- Immunosuppressants (e.g., Methotrexate, Azathioprine) to calm overactive immunity
- Corticosteroids for acute inflammation
- Biologics targeting specific immune pathways (e.g., TNF inhibitors in RA)
- Hormone replacement therapy (like thyroxine in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis)
2. Lifestyle & Nutrition
- Anti-inflammatory diet: rich in omega-3, antioxidants, fresh fruits & vegetables
- Adequate sleep, stress reduction, yoga, and meditation
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol
- Maintain a healthy body weight
3. Regular Monitoring
Routine check-ups and lab monitoring help manage medication effects and detect flares early.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Unexplained fatigue and joint pain lasting >2 weeks
- Recurrent rashes or mouth ulcers
- Persistent digestive problems
- Abnormal thyroid levels or sudden weight changes
- Numbness or weakness in limbs
Early detection helps prevent irreversible organ damage and improves long-term quality of life.
Autoimmune diseases remind us of how delicate the balance of our immune system is — a mechanism meant to protect us can sometimes turn into an internal aggressor.
Awareness, early diagnosis, and lifestyle care are the pillars of living well with these chronic conditions.
Remember: with medical guidance, mindfulness, and consistent care, autoimmune diseases can be managed — not feared.
References