Understanding Aarskog Syndrome: A Rare Genetic Puzzle
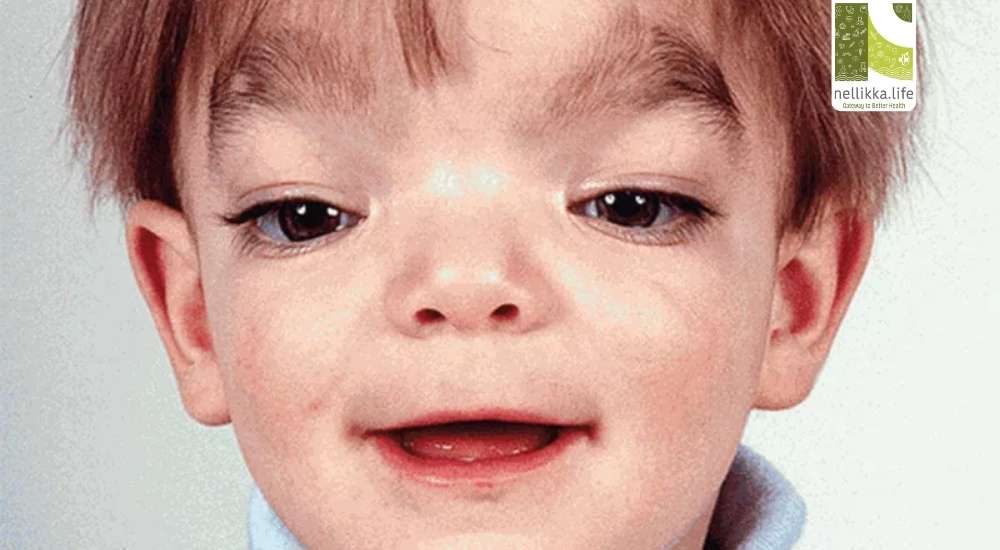
Aarskog Syndrome, also known as Aarskog-Scott syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder that affects physical development, particularly in males. Though often overlooked due to its mild presentation, this syndrome can have long-term implications for a child’s growth, development, and self-esteem. Let’s take a closer look at this condition—its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, complications, and management.
What is Aarskog Syndrome?
Aarskog Syndrome is a genetic condition primarily affecting the face, skeleton, muscles, and genitals. It is considered X-linked, meaning the gene responsible is located on the X chromosome and often affects males more severely. Females can be carriers and may show mild symptoms.
Causes
Aarskog Syndrome is caused by mutations in the FGD1 gene [1], located on the X chromosome (Xp11.21). This gene provides instructions for a protein involved in the development and function of many body systems, especially during fetal growth.
- Inheritance Pattern: X-linked recessive.
- Gene Affected: FGD1 (FacioGenital Dysplasia 1).
- Carriers: Females can carry the mutation and pass it on to offspring.
Symptoms
The symptoms of Aarskog Syndrome vary in severity and may become more noticeable as a child grows. The syndrome typically affects multiple parts of the body.
1. Facial Features
- Wide-set eyes (hypertelorism)
- Rounded face
- Small nose with a broad nasal bridge
- Long philtrum (space between the nose and upper lip)
- Widow’s peak hairline
2. Skeletal Abnormalities
- Short stature or delayed growth
- Short fingers and toes (brachydactyly)
- Broad hands and feet
- Joint laxity (loose joints)
- Mild chest deformities
3. Genital and Reproductive
- Shawl scrotum (testicles surrounded by excess skin)
- Undescended testicles (cryptorchidism)
- Small penis
4. Dental and Eye Issues
- Delayed eruption of teeth
- Crossed eyes (strabismus)
- Drooping eyelids (ptosis)
5. Cognitive and Behavioral
- Mild to moderate learning difficulties
- Hyperactivity
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
Exams and Tests
Diagnosing Aarskog Syndrome can be complex due to overlapping features with other syndromes. A combination of clinical evaluation, family history, and genetic testing is used.
Diagnostic Process:
- Physical Examination: Facial and skeletal features observed by a geneticist or pediatrician.
- Family History: To determine inheritance patterns.
- Genetic Testing: DNA analysis to detect FGD1 gene mutations.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays for skeletal abnormalities.
- Endocrinological Tests: To check growth hormone levels if short stature is severe.
Possible Complications
Though many children with Aarskog Syndrome lead relatively normal lives, complications can arise depending on the severity of the condition:
- Psychosocial Issues: Low self-esteem due to appearance or stature.
- Speech and Learning Delays
- Vision Problems
- Delayed Puberty
- Dental Issues: Misaligned or delayed teeth
When to Contact a Medical Professional
You should contact your doctor if:
- Your child shows multiple signs of delayed growth or unusual facial/skeletal features.
- There is a family history of Aarskog Syndrome.
- Developmental milestones (speech, motor skills) are delayed.
- Genital abnormalities are present at birth.
Early diagnosis and intervention (e.g., physical therapy, speech therapy, counseling) can help improve quality of life.
Is There a Way to Prevent It?
Since Aarskog Syndrome is genetic, there is no known way to prevent it. However, genetic counseling is highly recommended for:
- Women with a family history of Aarskog Syndrome.
- Parents who have had one child with the condition and are planning more.
Alternative Names for Aarskog Syndrome
- Aarskog-Scott Syndrome
- Faciodigitogenital Syndrome
- Faciogenital Dysplasia
These terms all refer to the same condition and may appear in older literature or in international medical settings.
Takeaway
Aarskog Syndrome may be rare, but understanding it can make a significant difference in the life of a child. Early diagnosis, supportive therapy, and proper medical care allow most children to thrive. Awareness is key—not just for affected families, but for society to create an inclusive and informed support system.
References
1. Faciogenital Dysplasia
2. Intelligence and development in Aarskog syndrome
3.AARSKOG-SCOTT SYNDROME; AAS