Demystifying Arthritis: Types, Symptoms, Affected Joints, Self-Care, and Treatment
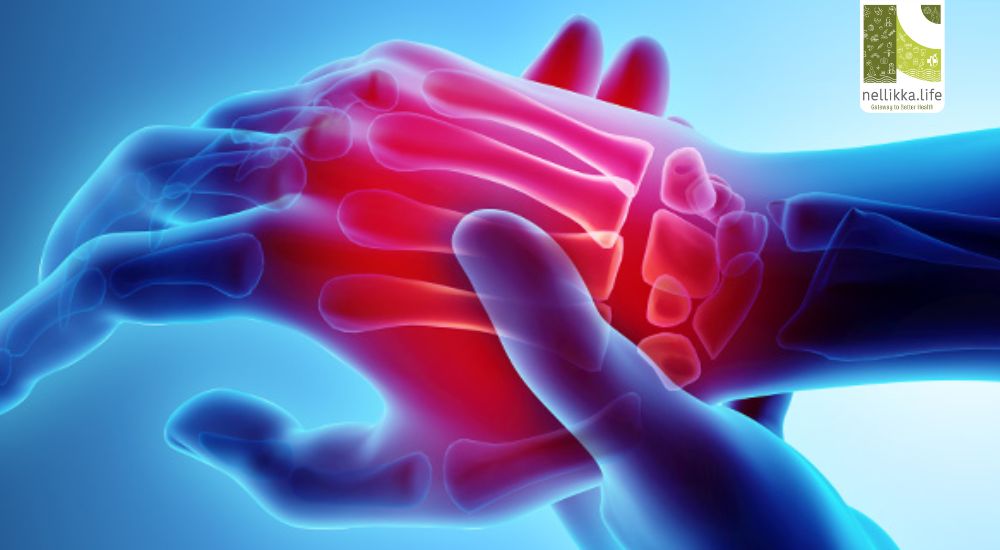
Arthritis is not a single disease but a broad term that refers to joint inflammation and stiffness affecting people of all ages, sexes, and backgrounds. It is one of the leading causes of disability worldwide, interfering with the ability to perform everyday tasks and impacting quality of life. Understanding arthritis can empower individuals to manage their condition effectively and seek timely treatment.
What Are the Different Types of Arthritis?
There are more than 100 types of arthritis, but the most common forms include:
1. Osteoarthritis (OA)
- The most common form, caused by wear and tear of the joint cartilage over time.
- Often associated with aging or joint injuries.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- An autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the joint lining.
- Can cause systemic symptoms like fatigue and fever.
3. Psoriatic Arthritis
- Occurs in some individuals with psoriasis.
- Can affect skin, nails, and joints simultaneously.
4. Gout
- Caused by uric acid crystal buildup in joints, often due to diet.
- Characterized by sudden and severe pain, often in the big toe.
5. Ankylosing Spondylitis
- A chronic inflammatory condition primarily affecting the spine and sacroiliac joints.
- Can lead to spinal fusion if untreated.
6. Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
- Affects children under the age of 16.
- Can impair growth and joint development.
What Are the Symptoms of Arthritis?
Symptoms can vary depending on the type of arthritis, but common signs include:
- Joint pain and stiffness
- Swelling and redness around the joints
- Reduced range of motion
- Fatigue, particularly in inflammatory types like RA
- Warmth in joints (inflammatory arthritis)
- Morning stiffness lasting longer than an hour
Which Joints Are Most Commonly Affected?
The joints affected depend on the type of arthritis:
- Osteoarthritis: Knees, hips, hands, spine
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Hands, wrists, knees, feet (usually symmetrically)
- Gout: Big toe, ankles, knees
- Psoriatic arthritis: Fingers, toes, spine
- Ankylosing spondylitis: Spine, hips, shoulders
What Are Some Self-Care Strategies for Arthritis?
Managing arthritis requires a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. Self-care plays a vital role in reducing symptoms and improving quality of life:
1. Healthy Diet
- Include anti-inflammatory foods: berries, leafy greens, fatty fish (rich in omega-3), turmeric.
- Avoid high-purine foods (in gout), processed foods, and excessive sugar.
2. Regular Exercise
- Low-impact activities like swimming, walking, and yoga help improve flexibility and strengthen muscles.
- Helps maintain a healthy weight, which reduces stress on joints.
3. Stress Management
- Chronic stress may worsen autoimmune arthritis.
- Meditation, mindfulness, and breathing exercises can help manage pain perception.
4. Hot and Cold Therapy
- Heat soothes stiff joints and muscles.
- Cold packs reduce inflammation and swelling.
5. Joint Protection Techniques
- Use ergonomic tools and maintain good posture.
- Avoid repetitive motions that strain affected joints.
How Is Arthritis Treated?
Treatment depends on the type and severity of arthritis and often involves a multidisciplinary approach:
1. Medications
- NSAIDs: To reduce pain and inflammation (e.g., ibuprofen, naproxen).
- DMARDs: For autoimmune forms like RA (e.g., methotrexate).
- Biologic Agents: Target specific parts of the immune system (e.g., TNF inhibitors).
- Steroids: Short-term use to control severe inflammation.
2. Injections
- Corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid can be injected directly into joints.
3. Physical and Occupational Therapy
- Strengthens muscles and teaches joint-sparing techniques.
4. Surgical Options
- Joint replacement (hip or knee) in severe cases.
- Arthroscopy or joint fusion may be recommended in specific scenarios.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience persistent joint pain, stiffness, or swelling lasting more than a few days, it’s essential to consult a rheumatologist. Early diagnosis and intervention can prevent permanent joint damage and improve long-term outcomes.
Living with arthritis can be challenging, but with the right knowledge, support, and treatment strategies, individuals can lead active and fulfilling lives. Embrace early detection, holistic management, and lifestyle choices that support joint health.
References :
1. Arthritis
2.Overview of Arthritis
3. About Arthritis
4. Arthritis Disease Information





